The speed at which material is extruded is influenced by several factors, including feed rate, screw design, pressure, barrel temperature, and cooling systems.
Types of Extrusion
In the realm of material science and manufacturing, extrusion stands as a prominent method for shaping materials. This section delves into the various types of extrusion methods, specifically focusing on Cold Extrusion, Hot Extrusion, and Micro Extrusion. Understanding these types can help in selecting the most suitable method for a given application.
Cold Extrusion
Cold extrusion is a process that occurs at or near room temperature. This type of extrusion is generally used for softer materials like aluminum, tin, and lead.
- Advantages
- High dimensional accuracy
- Smooth surface finish
- Energy-efficient since it doesn’t require heating
- Applications
- Making tubes and pipes
- Electrical wiring
- Beverage cans
- Key Factors Affecting Material Speed
- Lubrication
- Die design
- Material composition
Hot Extrusion
In contrast to cold extrusion, hot extrusion involves the heating of material above its recrystallization temperature. This process is most commonly used for metals that are difficult to shape at room temperature.
- Advantages
- Easier to work with harder materials
- Improved mechanical properties due to grain refinement
- More intricate geometries can be achieved
- Applications
- Structural components in the aerospace industry
- High-strength parts in automotive applications
- Railroad tracks
- Key Factors Affecting Material Speed
- Heating temperature
- Die geometry
- Ram speed
Micro Extrusion
Micro extrusion specializes in the fabrication of microscale and nanoscale components. This type of extrusion is crucial for high-precision applications, often found in medical and electronic industries.
- Advantages
- Extremely high precision
- Ability to handle complex geometries
- Suitable for delicate materials
- Applications
- Medical tubing
- Microfluidic devices
- Semiconductor components
- Key Factors Affecting Material Speed
- Feed rate
- Micro-die design
- Material viscosity
Material Properties
In any extrusion process, the properties of the material you are working with will heavily influence how quickly the material can be extruded. These properties can include viscosity, elasticity, and thermal conductivity. Let’s dive into each one to understand their role in the extrusion process.
Viscosity
Viscosity refers to the resistance of a fluid to deformation or flow. In extrusion, it plays a critical role in determining how easily a material can be pushed through a die.
- Importance in Extrusion
- High viscosity makes the material harder to extrude.
- Low viscosity may lead to material leakages.
- Factors Influencing Viscosity
- Temperature
- Shear rate
- Polymer molecular weight
- How to Measure Viscosity
- Rotational viscometers
- Capillary rheometers
Elasticity
Elasticity is the ability of a material to return to its original shape after deformation. In the extrusion process, it can impact the material’s behavior as it flows through the die.
- Importance in Extrusion
- High elasticity may cause material to rebound after passing through the die, affecting its shape.
- Low elasticity may result in permanent deformation, which could be undesirable.
- Factors Influencing Elasticity
- Material composition
- Temperature
- Processing speed
- How to Measure Elasticity
- Tensile tests
- Dynamic mechanical analysis

Thermal Conductivity
Thermal conductivity is a measure of a material’s ability to conduct heat. It can affect how quickly a material reaches its ideal extrusion temperature.
- Importance in Extrusion
- High thermal conductivity allows for quicker heating and more uniform temperature distribution.
- Low thermal conductivity can lead to longer startup times and uneven material flow.
- Factors Influencing Thermal Conductivity
- Material composition
- Ambient temperature
- Cooling system efficiency
- How to Measure Thermal Conductivity
- Laser flash analysis
- Hot wire method
Machine Parameters
The machine’s components and settings significantly affect the rate of material extrusion. We’ll focus on three key aspects: Screw Design, Barrel Temperature, and Motor Speed. A thorough understanding of these parameters can drastically improve the efficiency and quality of your extrusion process.
Screw Design
Screw design is crucial in determining how well the machine mixes, melts, and propels material through the barrel.
- Importance in Extrusion
- A well-designed screw ensures uniform melting and mixing of the material.
- A poorly designed screw can lead to inconsistent material properties, affecting the end product quality.
- Factors Influencing Screw Design
- Screw diameter
- Helix angle
- Compression ratio
- How to Optimize Screw Design
- Use Computational Fluid Dynamics simulations
- Conduct small-scale testing

Barrel Temperature
Barrel temperature plays a vital role in material flow and quality in the extrusion process.
- Importance in Extrusion
- Too high a temperature may degrade the material or cause safety hazards.
- Too low a temperature can lead to incomplete melting and poor material flow.
- Factors Influencing Barrel Temperature
- Material thermal properties
- Ambient temperature
- Extrusion speed
- How to Control Barrel Temperature
- Use thermocouples for precise temperature measurements
- Implement PID controllers for automated temperature control
Motor Speed
Motor speed controls how quickly the screw turns, influencing the rate at which material is extruded.
- Importance in Extrusion
- High motor speed can lead to quicker extrusion but may compromise material quality.
- Low motor speed can yield higher quality but reduces throughput.
- Factors Influencing Motor Speed
- Material viscosity
- Screw design
- Power limitations
- How to Optimize Motor Speed
- Use variable-frequency drives for adjustable speed control
- Monitor amperage to prevent motor overload
Process Variables
Process variables are a set of conditions that can be adjusted in real-time during the extrusion process to control how quickly material is extruded. We’ll delve into three critical variables: Feed Rate, Pressure, and Cooling System. Understanding these variables can help you fine-tune your process for maximum efficiency and quality.
Feed Rate
Feed rate refers to the speed at which raw material is fed into the extruder. It has a direct impact on the overall speed and efficiency of the extrusion process.
- Importance in Extrusion
- High feed rates can increase production speed but may lead to inconsistent quality.
- Low feed rates can improve quality but may decrease throughput.
- Factors Influencing Feed Rate
- Material viscosity
- Screw design
- Hopper design
- How to Optimize Feed Rate
- Use feed rate controllers for automated adjustments
- Monitor material flow visually or through sensors
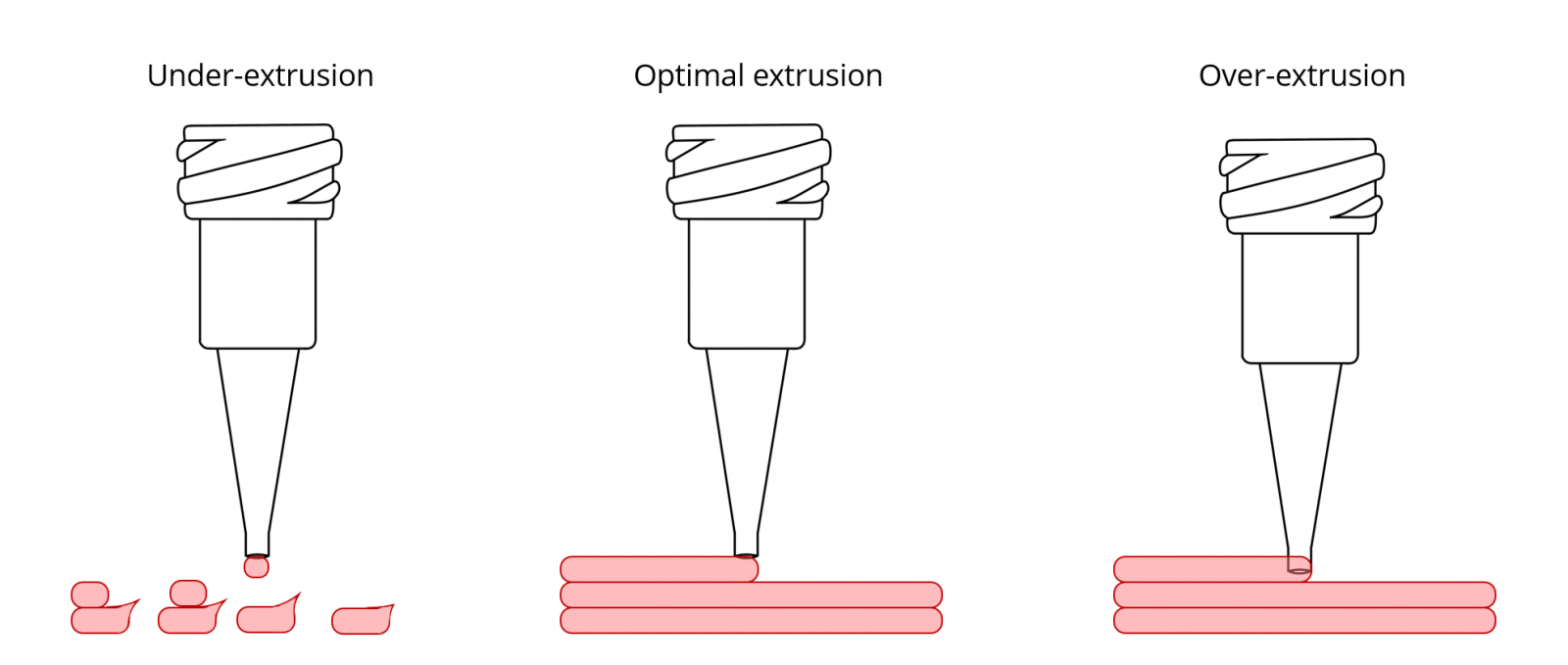
Pressure
Pressure is an essential variable that determines how hard the material is pushed through the extruder.
- Importance in Extrusion
- High pressure ensures a smooth flow of material but may cause equipment wear.
- Low pressure might result in incomplete extrusion and wasted material.
- Factors Influencing Pressure
- Barrel temperature
- Material viscosity
- Die design
- How to Monitor and Control Pressure
- Use pressure gauges or sensors
- Implement safety valves for pressure release
Cooling System
The cooling system helps in regulating the temperature of the extruded material as it exits the die, affecting its final properties.
- Importance in Extrusion
- Efficient cooling can speed up production and improve material properties.
- Inadequate cooling can result in defects like warping or dimensional inaccuracies.
- Factors Influencing Cooling Efficiency
- Material thermal conductivity
- Environmental conditions
- Cooling medium
- How to Optimize the Cooling System
- Use variable-speed fans or water-cooling systems
- Regularly clean and maintain the cooling system to ensure efficiency

External Factors
External factors might not be a direct part of the extrusion machinery or material, but they can significantly impact how quickly and efficiently the material is extruded. We’ll look at three such factors: Ambient Temperature, Humidity, and Operator Skill Level.
Ambient Temperature
Ambient temperature refers to the temperature of the surrounding environment where the extrusion is taking place.
- Importance in Extrusion
- High ambient temperatures can cause the material to pre-heat, affecting its behavior in the extruder.
- Low ambient temperatures might require additional energy to bring the material to the ideal extrusion temperature.
- Factors Influencing Ambient Temperature
- Geographic location
- Season
- Climate control systems
- How to Manage Ambient Temperature
- Use HVAC systems for temperature control
- Monitor ambient temperature continuously for adjustments
Humidity
Humidity, or the amount of moisture in the air, can also affect the extrusion process.
- Importance in Extrusion
- High humidity can cause some materials to absorb moisture, affecting their viscosity.
- Low humidity might lead to static electricity, which can disrupt the process.
- Factors Influencing Humidity
- Weather conditions
- Time of year
- Dehumidifiers
- How to Control Humidity
- Use dehumidifiers or humidifiers based on needs
- Store material in climate-controlled spaces
Operator Skill Level
The skill level of the machine operator plays a vital role in determining how well the extrusion process is managed.
- Importance in Extrusion
- Skilled operators can identify and solve problems quickly, optimizing the process.
- Inexperienced operators may make mistakes that slow down production or compromise quality.
- Factors Influencing Operator Skill Level
- Training
- Experience
- Certifications
- How to Improve Operator Skill Level
- Provide ongoing training and skill development programs
- Implement mentorship programs for new operators
Optimization Strategies
Optimization strategies are a collection of techniques aimed at improving the efficiency and effectiveness of the extrusion process. In this section, we discuss three pivotal strategies: Design of Experiments, Process Monitoring, and Feedback Control Systems. Utilizing these methods can bring about measurable improvements in your extrusion process.
Design of Experiments
Design of Experiments (DoE) is a structured approach to determining the relationship between factors affecting a process and the output of that process.
- Importance in Extrusion
- Allows for systematic exploration of all variable interactions.
- Identifies the most significant factors affecting the extrusion rate.
- Factors Included in DoE
- Material properties
- Machine parameters
- Process variables
- How to Implement DoE
- Use statistical software for experimental design
- Analyze the collected data to draw inferences and make improvements

Process Monitoring
Process Monitoring involves continuously observing the extrusion process to make real-time adjustments.
- Importance in Extrusion
- Enables early identification of issues, minimizing downtime.
- Helps maintain consistent quality and throughput.
- Monitoring Tools
- Sensors
- Cameras
- Data analytics platforms
- How to Implement Process Monitoring
- Install necessary monitoring devices
- Use software to analyze the data and make recommendations
Feedback Control Systems
Feedback control systems use real-time data to make adjustments to the process variables automatically.
-
- Importance in Extrusion
- Maintains a stable extrusion process by continuously adapting to changes.
- Reduces the reliance on manual adjustments, saving time and labor.
- Components of a Feedback Control System
- Sensors
- Controllers
- Actuators
- How to Implement Feedback Control Systems
- Choose appropriate sensors and actuators for your specific needs
- Use software to create control algorithms
- Importance in Extrusion




