Acrylic is used in injection moulding for its clarity, UV resistance, lightweight properties, and design flexibility.

Advantages of Using Acrylic in Injection Moulding
Transparency and Clarity
- Acrylic offers a glass-like transparency, making it suitable for clear or see-through applications.
- Products made of acrylic allow for excellent light transmission, giving them a premium look.
- Ideal for manufacturing items like eyeglasses, aquariums, and display cases due to its high optical clarity.
Resistance to UV Light and Weathering
- Acrylic products can withstand long-term UV exposure without yellowing or becoming brittle.
- Provides extended longevity to outdoor items such as solar panels, skylights, and outdoor signage.
- Unlike certain plastics, acrylic doesn’t easily degrade, ensuring a longer life for outdoor applications.
Lightweight and Sturdiness
- Acrylic components are lighter than glass, making transportation and installation easier.
- The material combines rigidity with lightweight properties, ensuring products are both strong and easy to handle.
- It’s a favorite choice in industries where both strength and weight are vital considerations, like aviation.
Flexibility in Design and Coloring
- Acrylic is adaptable to various molding techniques, allowing for intricate designs and detailed patterns.
- The material accepts colors well, leading to bright, fade-resistant products.
- Designers have the freedom to experiment with shades and forms, thanks to acrylic’s flexible nature, making it popular in industries such as toy manufacturing and home decor.
Comparison with Other Materials
Acrylic vs. Polycarbonate
| Feature | Acrylic | Polycarbonate |
|---|---|---|
| Optical Clarity | ✔ Superior clarity, often used for cosmetic displays and aquariums. | ✔ Good clarity, but can have a slight tint. |
| UV Resistance | ✔ Naturally UV resistant, doesn’t yellow easily. | ❌ Requires a UV stabilizer or coating to resist yellowing. |
| Impact Resistance | ❌ Can break or shatter upon hard impact. | ✔ Very high impact resistance, used for bulletproof windows. |
| Weight | ✔ Lightweight, similar to other plastics. | ✔ Lightweight but slightly heavier than acrylic. |
| Flexibility | ❌ Less flexible and can crack under force. | ✔ High flexibility and bendability without breaking. |
Acrylic vs. PET
| Feature | Acrylic | PET |
|---|---|---|
| Optical Clarity | ✔ Superior clarity, ideal for display purposes. | ✔ Clear but not as transparent as acrylic. |
| Food Safety | ❌ Generally not used for food containers. | ✔ Commonly used for food packaging like water bottles. |
| Recyclability | ❌ Less commonly recycled. | ✔ Widely recycled, symbolized by the number “1” in the recycling triangle. |
| Cost | ❌ Typically more expensive. | ✔ Cost-effective and widely available. |
| Chemical Resistance | ✔ Resistant to many solvents. | ❌ Can be affected by strong acids or bases. |
Benefits of Choosing Acrylic over Alternatives
- Superior Optical Clarity: Acrylic offers unparalleled clarity, enhancing the aesthetic appeal of products.
- Natural UV Resistance: Unlike polycarbonate, acrylic doesn’t require any additives to resist UV radiation, maintaining its appearance for longer.
- Chemical Resistance: Acrylic stands up well against many common chemicals, making it ideal for various industrial applications.
- Ease of Fabrication: Acrylic can be easily shaped, molded, and tailored to specific requirements, offering more design freedom.
- Cost-effectiveness: While acrylic might be more expensive than PET, its durability, and other benefits can provide value for money in the long run.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Acrylic Recycling Processes
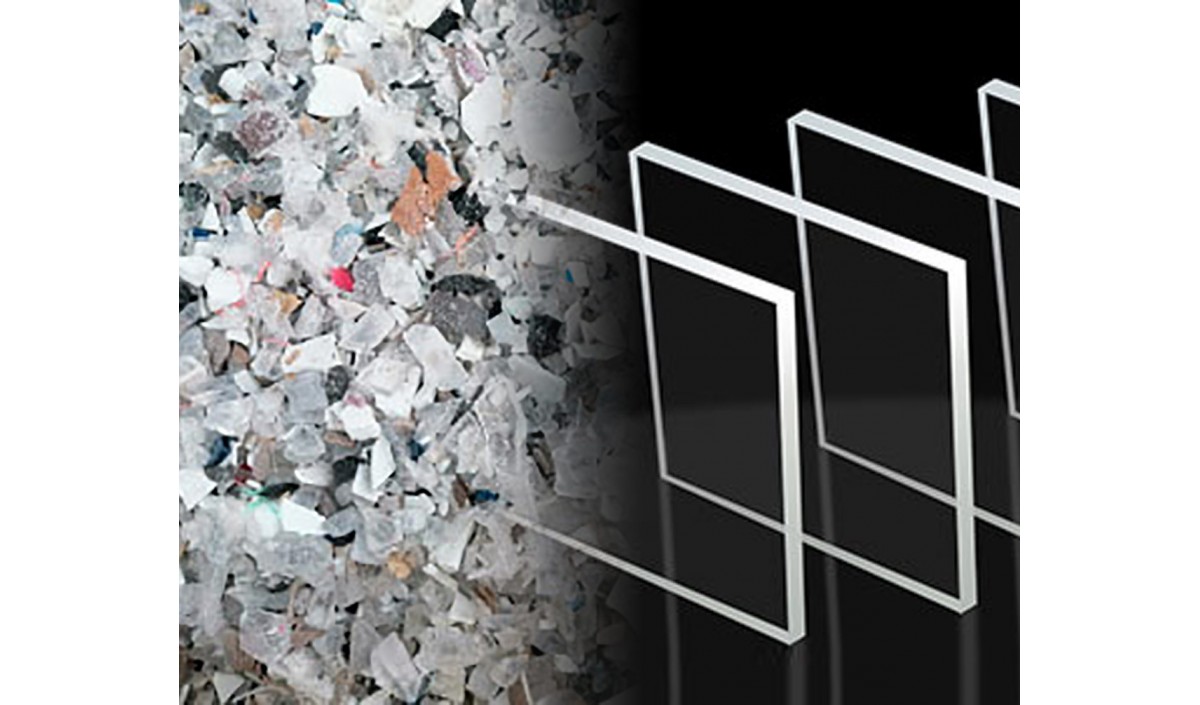
- Acrylic can be recycled through a process called chemical recycling. This involves breaking down the acrylic into its original monomers, which can then be repurposed to produce new acrylic products.
- While not as prevalent as the recycling of plastics like PET, facilities that handle acrylic recycling are growing in number.
- One method involves grinding acrylic scrap into a powder, which can then be reintroduced into the production process.
- By recycling acrylic, we can reduce the need for new raw materials, conserving resources and reducing environmental impact.
- There’s an increasing push towards creating a circular economy for acrylic, ensuring that end-of-life products are not wasted but instead reused in sustainable ways.
Carbon Footprint of Acrylic Production and Disposal
- The production of acrylic involves the polymerization of the monomer methyl methacrylate (MMA), a process that consumes energy and results in greenhouse gas emissions.
- While the carbon footprint of producing acrylic can be high, advancements in manufacturing technology are seeking ways to mitigate this impact.
- Disposal of acrylic in landfills can lead to long decomposition times, furthering its environmental footprint.
- The burning or incineration of acrylic can release harmful gases, emphasizing the importance of recycling as a sustainable disposal method.
- As consumers become more aware of environmental concerns, there’s an increasing demand for acrylic products sourced and produced through eco-friendly practices.
Applications and End Products
Acrylic in Automotive Industry
- Acrylic offers a clear advantage in producing high-quality, transparent car components like tail lights, headlights, and indicator lenses.
- Due to its UV resistance, acrylic parts in vehicles don’t yellow or degrade easily, ensuring a pristine look for longer.
- Its lightweight property contributes to the overall weight reduction of vehicles, which can lead to better fuel efficiency.
- Some luxury cars also use acrylic for panoramic sunroofs, offering a clear view while remaining strong and resistant to weathering.
- With advancements in electric vehicles and autonomous cars, the demand for acrylic components, especially in sensors and display panels, is on the rise.

Use in Consumer Electronics
- Acrylic finds its way into various consumer electronics, primarily due to its optical clarity and aesthetic appeal.
- It’s common to see acrylic in TV screens, computer monitors, and mobile device stands, providing a sleek and modern look.
- Transparent speaker enclosures and headphone parts often employ acrylic to showcase internal components as a design feature.
- Many virtual reality headsets utilize acrylic lenses to offer users a clear and immersive experience.
Home Decor and Furnishings
- Acrylic’s versatility shines in home decor, with its ability to mimic the appearance of glass while being more durable and lightweight.
- Items like photo frames, coffee tables, and decorative displays are often crafted from acrylic, giving interiors a modern touch.
- Due to its moldability, acrylic is also used to produce unique lighting fixtures and art installations.
- Acrylic aquariums are popular among enthusiasts as they provide clearer views than traditional glass tanks and are less prone to shattering.
Medical Equipment and Devices
- The medical industry values acrylic for its strength, clarity, and biocompatibility.
- Dental prosthetics, like dentures, often use acrylic resins for their natural appearance and durability.
- In ophthalmology, intraocular lenses made from acrylic materials are commonly implanted during cataract surgeries.
- Medical devices, such as IV drip chambers, benefit from acrylic’s clear and sturdy properties, allowing for easy monitoring of fluid levels.


